Here is the annual GDP growth rate since 1920 in black. The red line shows a three factor regression model. This tax policy model includes the influences of the top bracket from Figure G9, the top marginal rate from Figure G12 and the capital gains tax rate from Figure G13.
Here is the annual GDP growth rate since 1920 in black. The red line shows a three factor regression model. This tax policy model includes the influences of the top bracket from Figure G9, the top marginal rate from Figure G12 and the capital gains tax rate from Figure G13.
The model accounts for the linear correlation of the top bracket, the curvilinear correlations of the two tax rates and how the curvilinear correlations change as the top bracket rises. This model estimates that the current baseline growth rate for the economy is 1.1%.
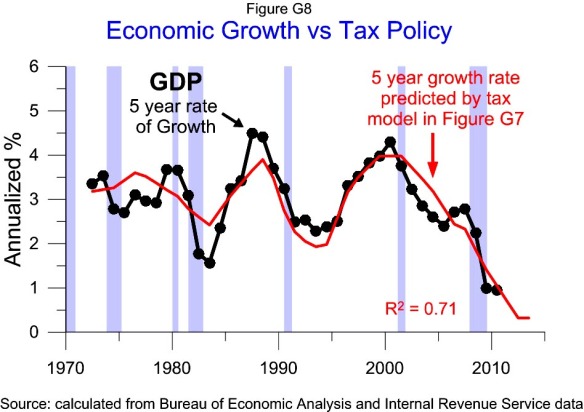
The annual growth fluctuates much more than the growth predicted by tax policy. Many of the other factors affecting annual growth may have little effect on the long term trend. Looking at the growth rate over 5 year periods as shown in Figure G15 may show more clearly the impact of tax policy on long term growth.